An induction furnace uses electromagnetic induction to bring steel billets to rolling temperature. It typically pairs with the rolling mill to form a billet heating & rolling line with closed-loop temperature control.

An SCR frequency converter supplies AC at the required frequency; a helical inductor creates an alternating magnetic field; eddy currents heat the billet volumetrically.
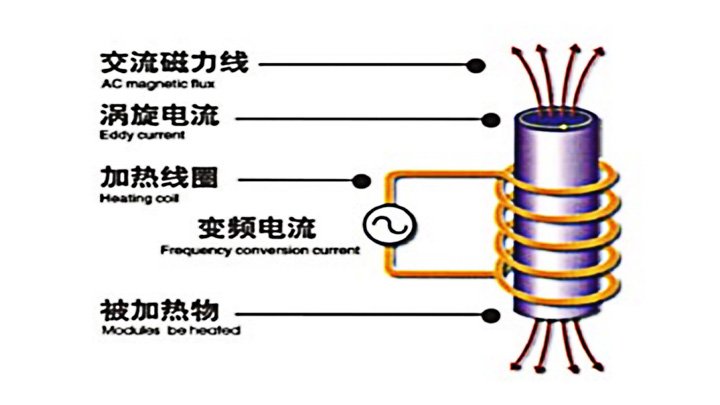
Billet materials: cast/carbon/alloy steels, cast iron; also stainless steels and non-ferrous alloys (Al/Cu). Shapes: round/square billets, tube hollows, slabs/plates.
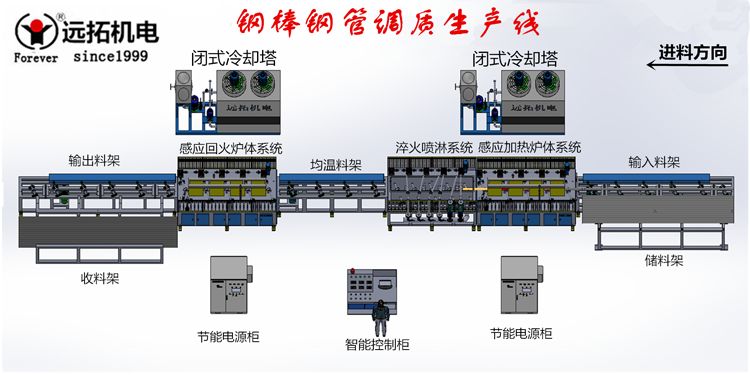
SCR power supply; induction coils (heating/stabilization zones); roller handling; PLC/HMI with IR pyrometers; closed-loop water-cooling.
Cold charge: ambient to ~1200 °C. Online reheating: ~800 °C to ~1200 °C (ΔT ≈ 400 °C). Final setpoints depend on chemistry, section, speed; validated by trials.
As a custom system, power is derived from throughput, start temperature, geometry, and efficiency. Rule-of-thumb: P (kW) ≈ 420 × G (t/h) from ambient to ~1200 °C; online reheating requires less.
Fast heating with uniform profile; precise IR closed loop; energy-efficient, no open flame; high automation & repeatability; flexible configuration.
Contact Yuantuo to size the power, calculate takt time, and plan your layout. We run billet trials and deliver turnkey systems.
© 2018 Hebei Yuantuo Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd. All rights reserved